Debian 7.0 (Wheezy) Release Candidate 1 was released on February 17th, 2013. This is not the final stable release, which expected in a few months. It is still a “testing” release (not recommended for production servers). However, it is a foretaste of the final (stable) version that will follow.
New features include Linux kernel 3.2 with longterm support, ext4 is now the default filesystem, systemd support. Read the full list here.
Here I will setup a Debian 7 system intended for LAMP server. “systemd” is a system and service manager for Linux, compatible with SysV and LSB init scripts. “systemd” has been adopted from many distributions. See why. So, I will activate it in the following setup. As an example, you will see:
systemctl restart apache2.service instead of
service apache2 restart.
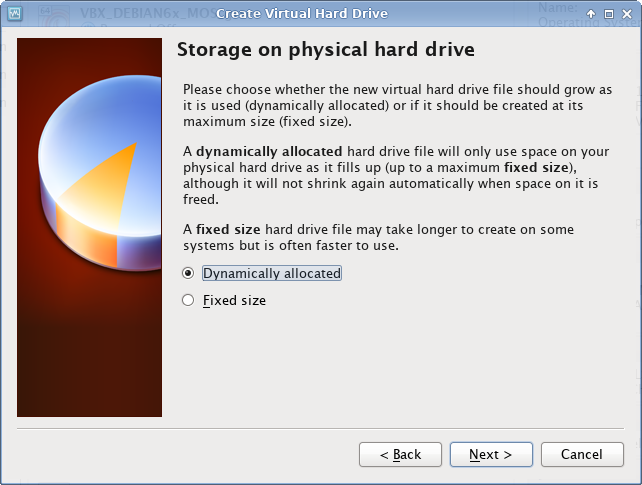
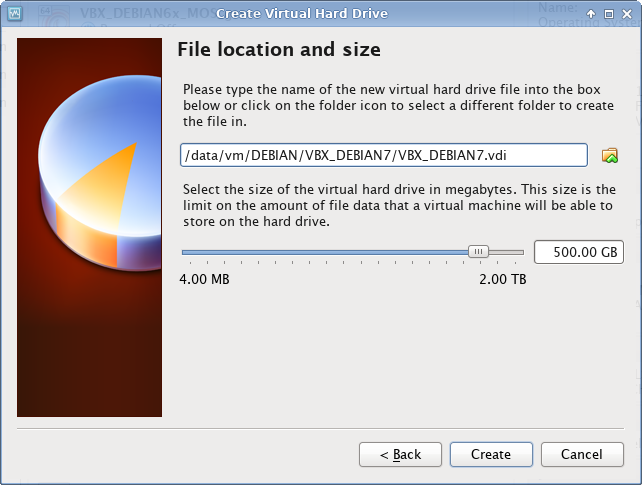
Create virtual machine
Debian 7 RC1 can be downloded from http://www.debian.org/devel/debian-installer/. I will use the netinst amd64 ISO image from here (about 230 MB).
Debian 7 RC1 amd64 will be installed in a virtual machine, using Virtualbox:
Start
Power on virtual machine will start Debian setup. Select boot from CD (pressing F12 during start-up.

If you need advanced configuration (e.g. creating Partition table), select
Advanced options → Expert install
Settings
Configure language, location and keyboard.
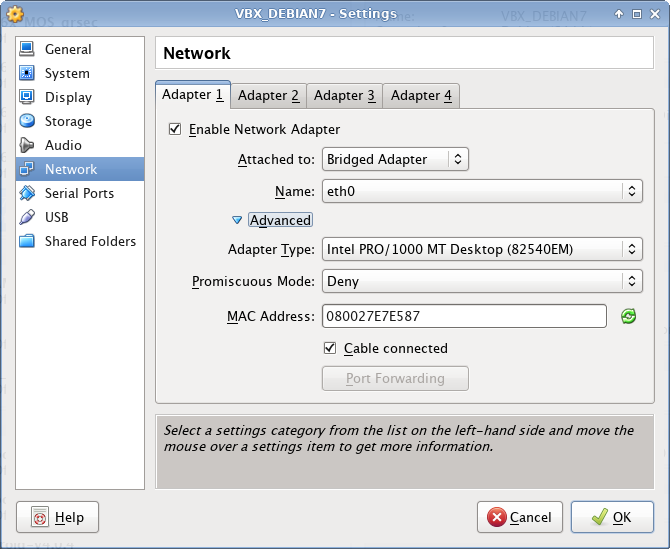
Network
Set Hostname and Domain
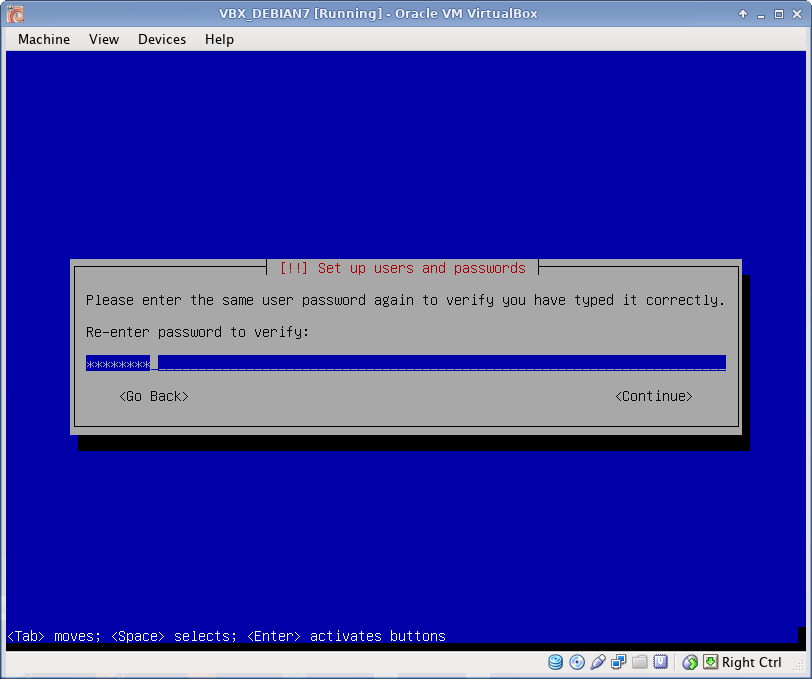
Users
Set root password and create a common user.
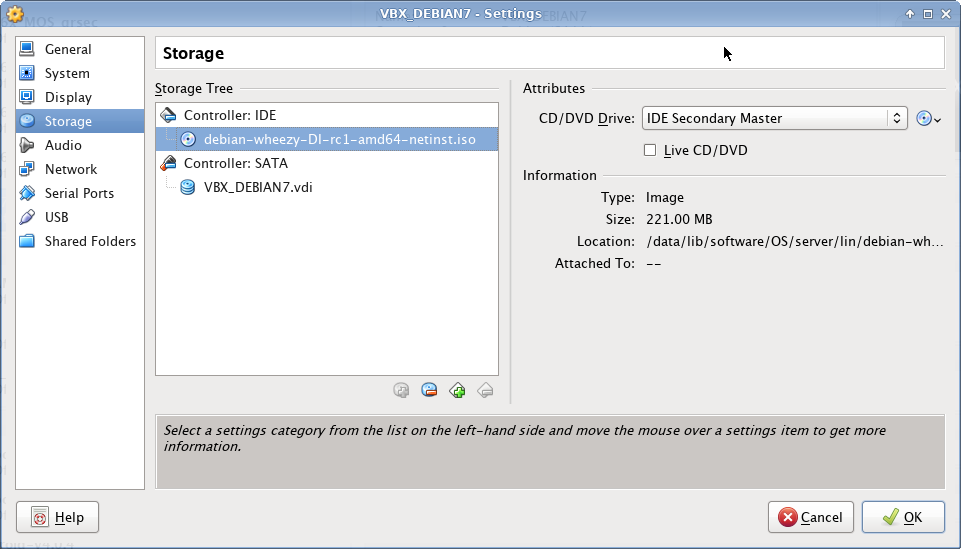
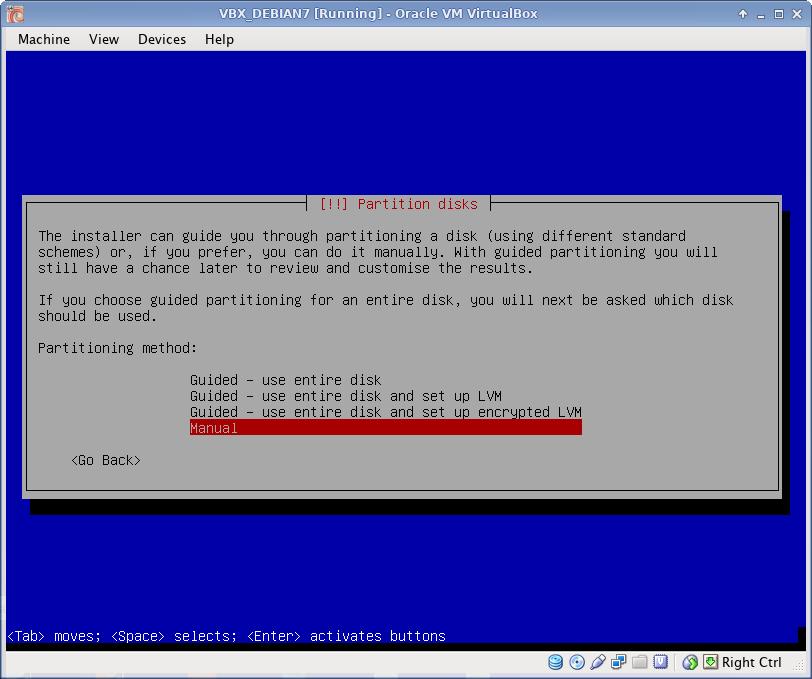
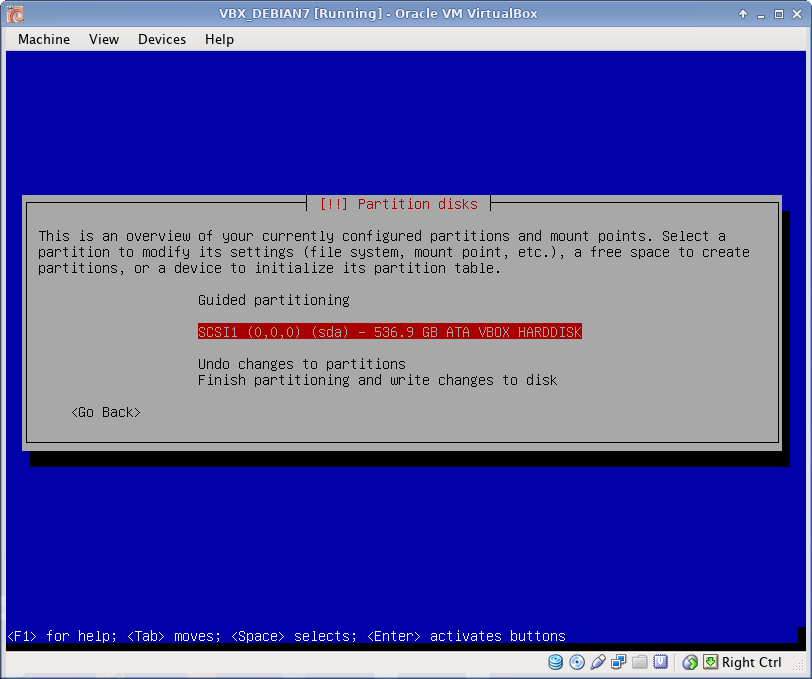
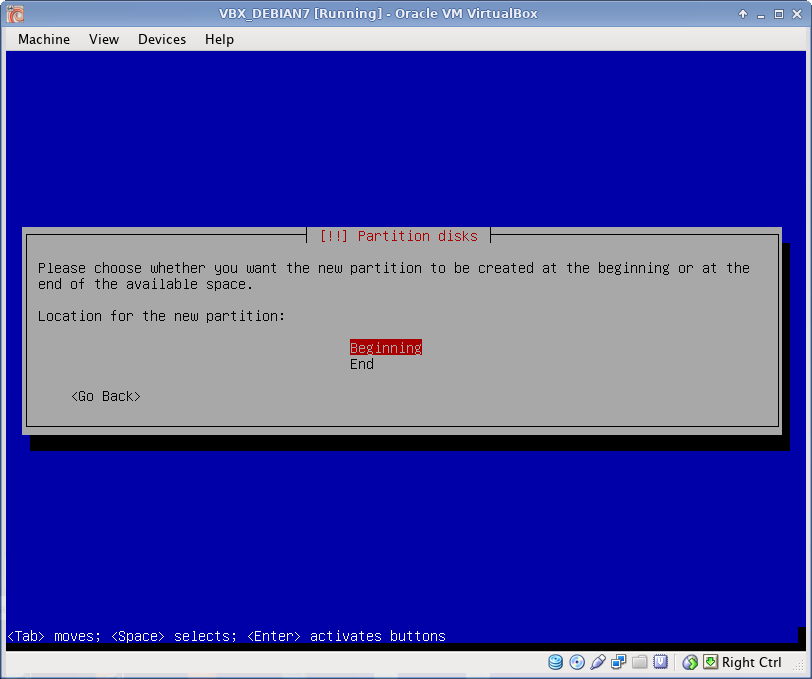
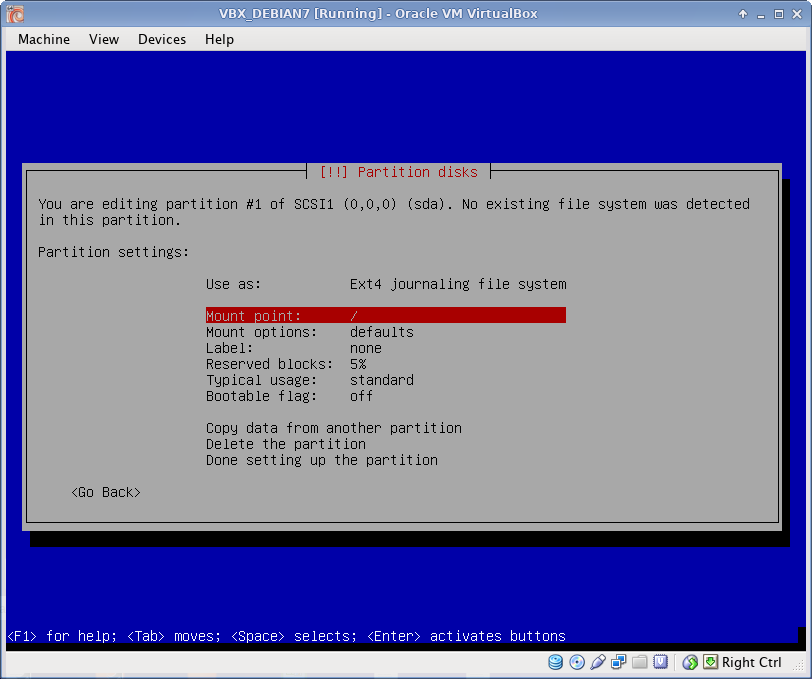
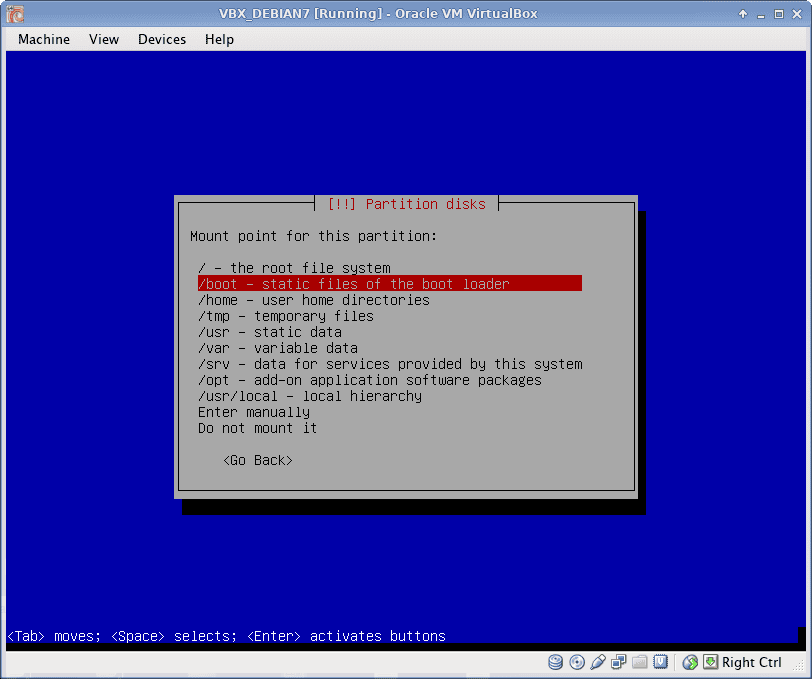
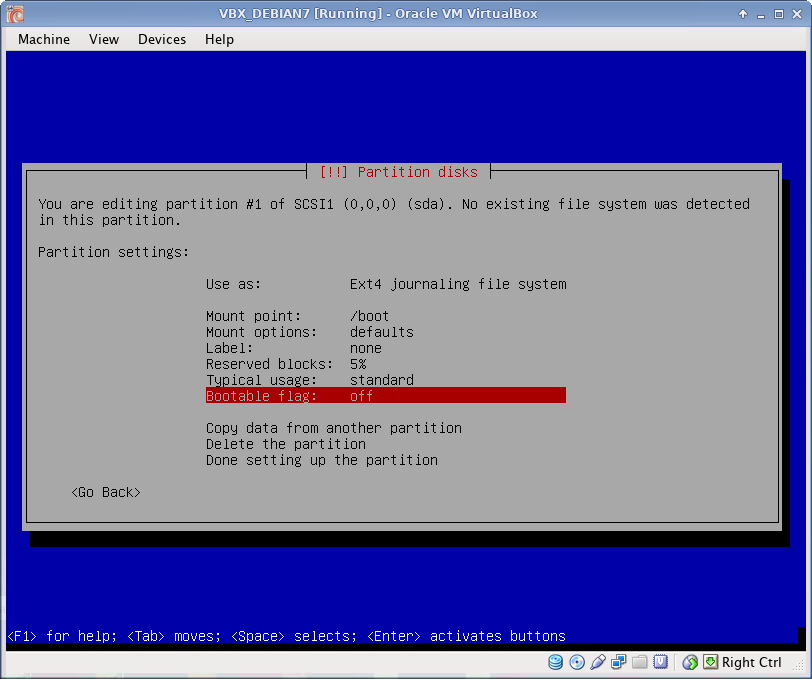
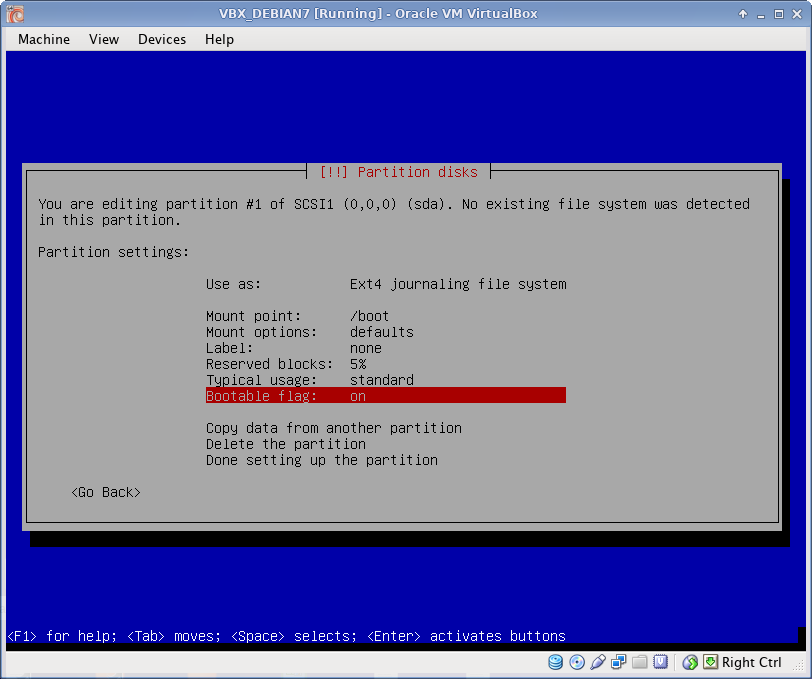
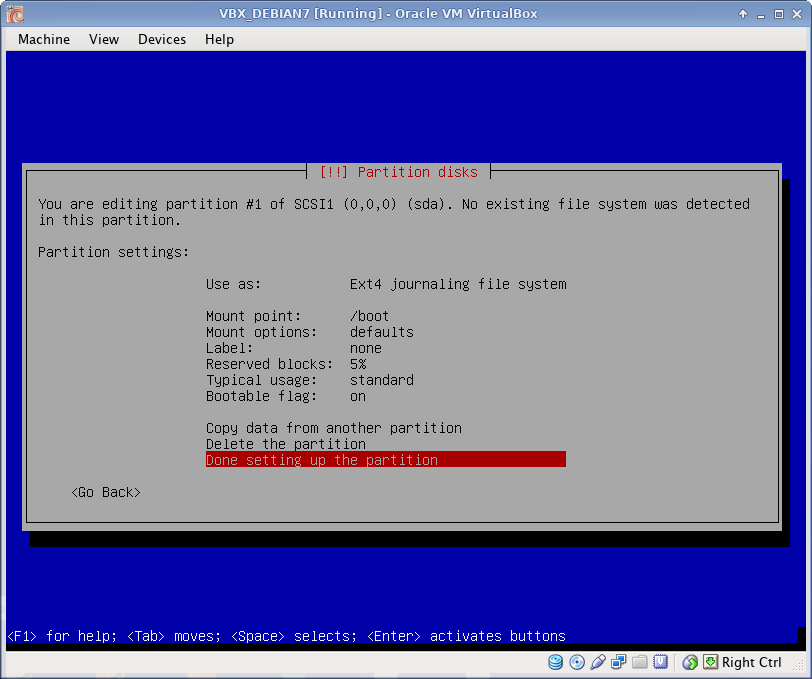
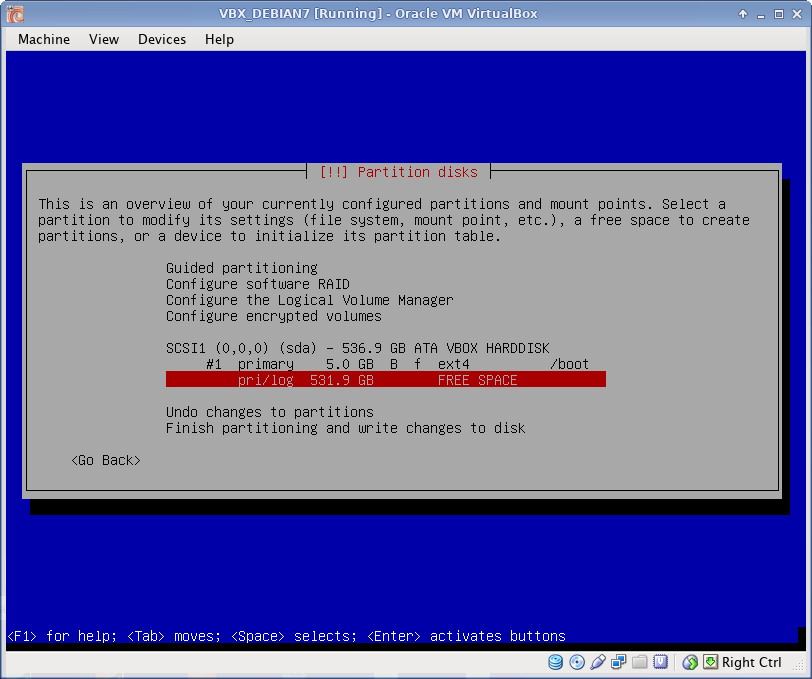
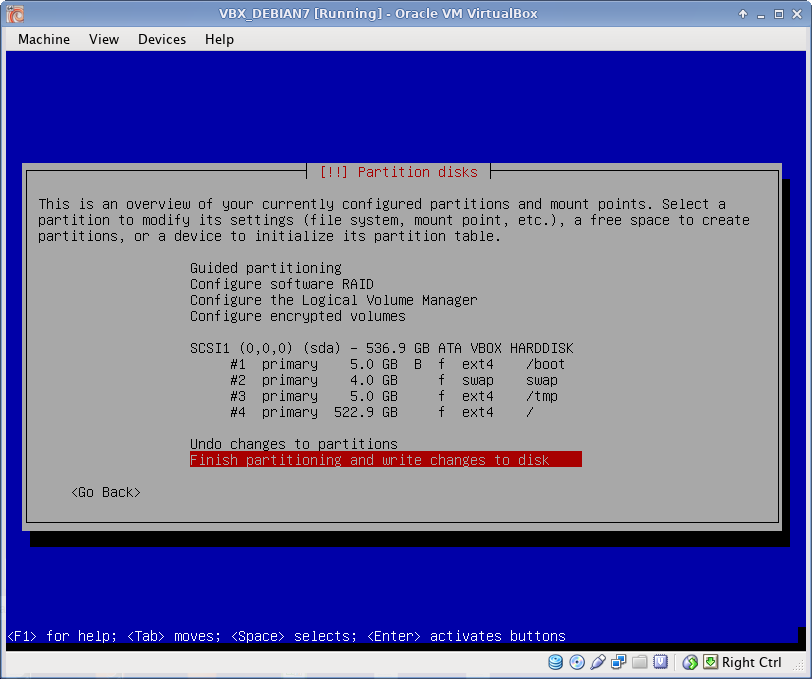
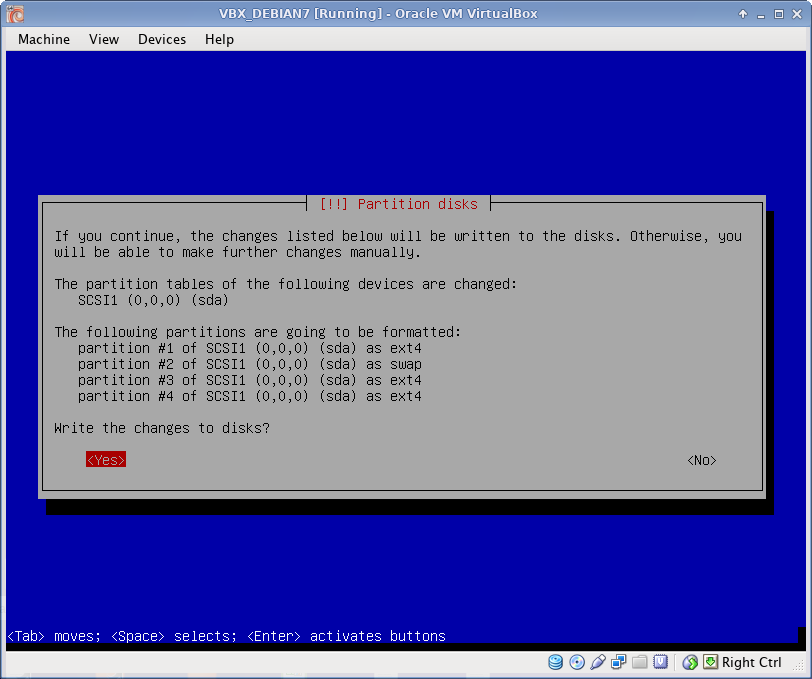
Disk Partitioning
I use EXT4 file system, which is default to Debian 7. All partitions are Primary. I prefer to create partitions manually, as following:
- /boot partition 5 GB
- swap partition 4 GB (usually RAM x 4)
- /tmp partition 5 GB
- / partition the rest of the disk from root partition
Below is described /boot partition creation in details. Rest partitions are created using the same procedure (only /boot partition has bootable flag ON).
Base system
Installing the base system.
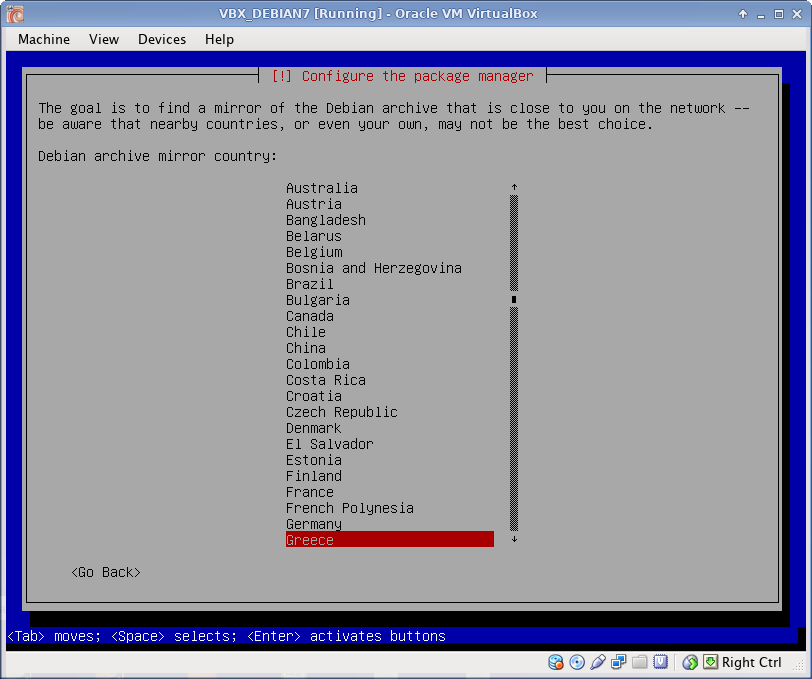
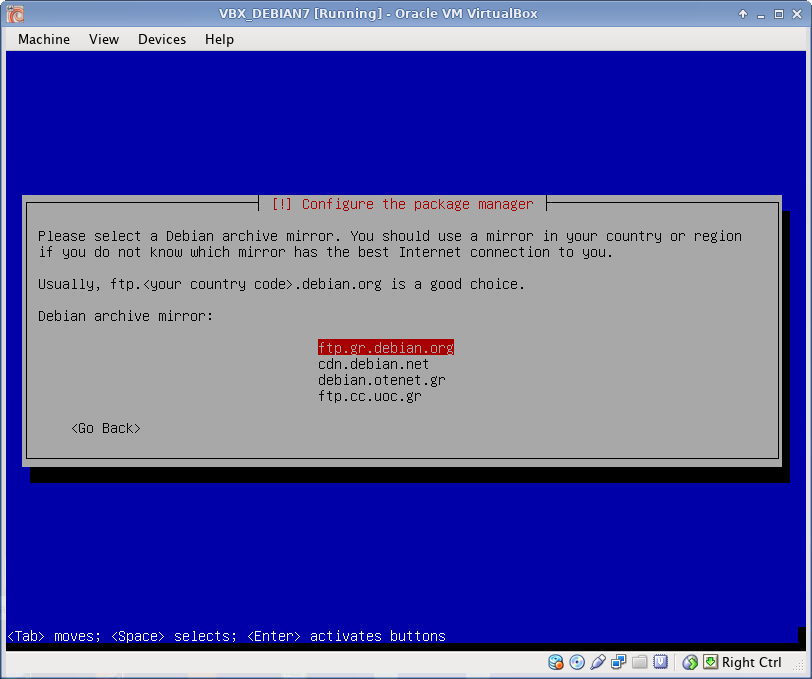
Package manager
Select Debian archive mirror and apt configuration.
Software installation
Software installation progress.
Popularity contest
Choose if you want to participate in Popularity contest.
Select additional software
After the installation of core system, additional software could be selected for installation. This is a server system, so only SSH server and Standard system utilities have been selected. Any additional software (web server, database server etc) will be installed manually after base installation (see below).
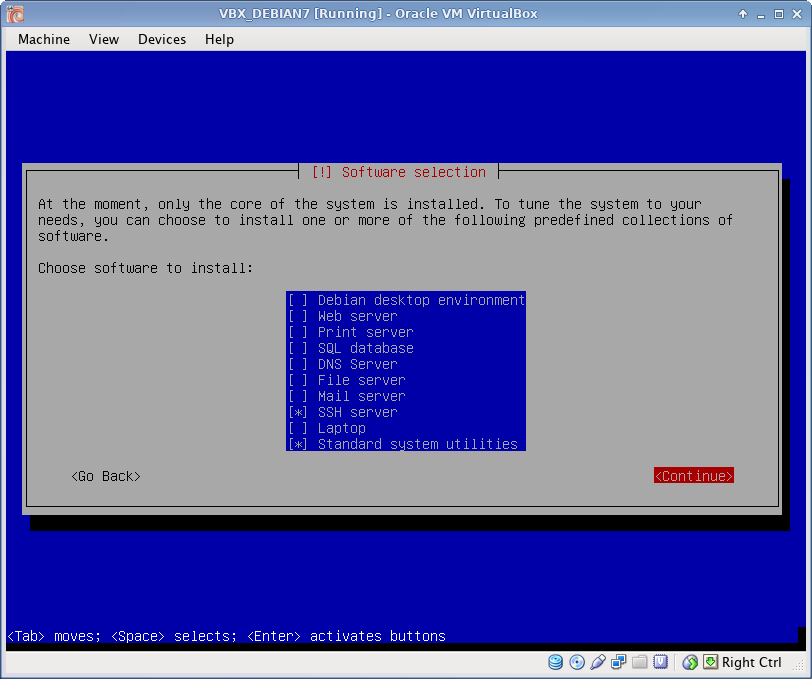
Install additional software
Additional software installation progress.
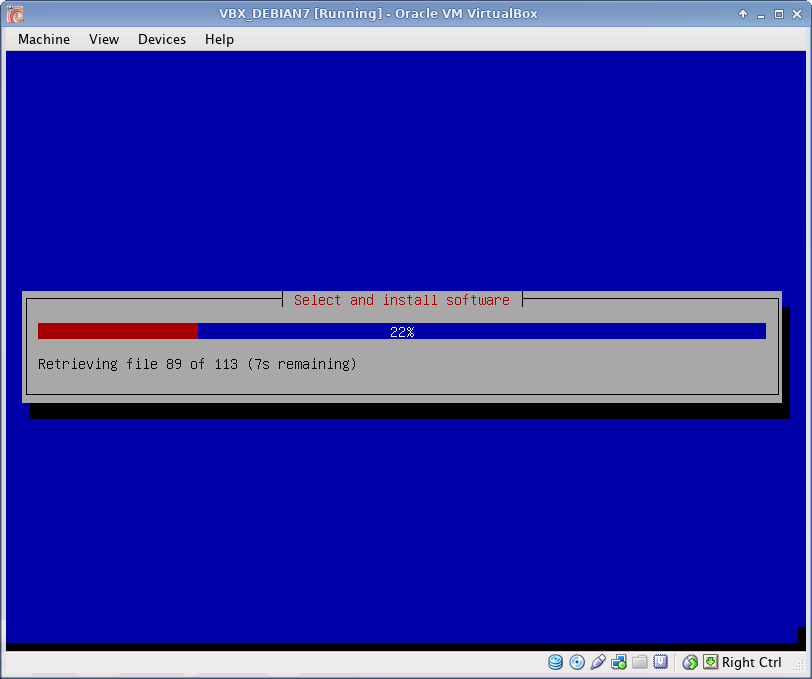
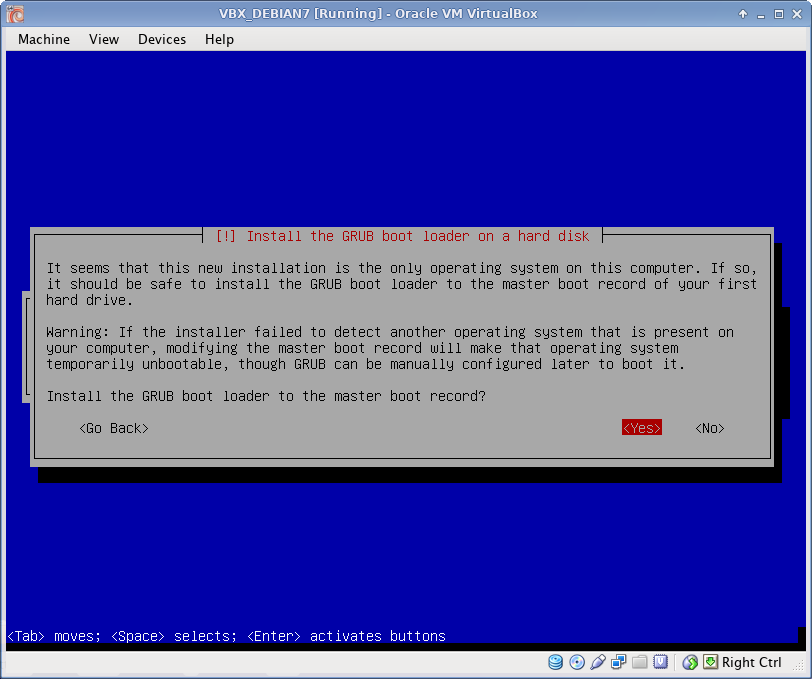
Grub boot loader
Grub boot loader installation.
Finish installation
Base Setup is finished. Reboot and login for first time.
Perform a system upgrade
Check your repositories definitions:
nano /etc/apt/sources.list
They must look like:
deb http://ftp.gr.debian.org/debian/ wheezy main
deb-src http://ftp.gr.debian.org/debian/ wheezy main
deb http://security.debian.org/ wheezy/updates main
deb-src http://security.debian.org/ wheezy/updates main
Perform system update:
apt-get update && apt-get -V upgrade
Install systemd
Using apt-get:
apt-get install systemd
Edit Grub options:
nano /etc/default/grub
Modify GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=”quiet” to:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet init=/bin/systemd"
Finally:
update-grub && reboot
Install time server
Using apt-get:
apt-get install ntp
Add static IP
To set the static IP 192.168.1.200 modify network configuration:
nano /etc/network/interfaces
Replace
allow-hotplug eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
with
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.1.200
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.1
Restart network
systemctl restart networking.service
Test results:
ip addr
Results must look like:
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:e7:e5:87 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.200/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eth0
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fee7:e587/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Harden SSH
Edit SSH configuration:
nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Make the following changes
...
PermitRootLogin no
...
X11Forwarding no
...
AllowUsers pontikis ...
...
Restart SSH
systemctl restart ssh.service
Install Webmin (optional)
According to http://www.webmin.com/deb.html:
Add Webmin repositories KEY:
wget http://www.webmin.com/jcameron-key.asc
apt-key add jcameron-key.asc
Modify repositories definitions:
nano /etc/apt/sources.list
Add Webmin repositories:
deb http://download.webmin.com/download/repository sarge contrib
deb http://webmin.mirror.somersettechsolutions.co.uk/repository sarge contrib
Update repositories:
apt-get update
Finally, install webmin:
apt-get install webmin
Test Webmin at: https://192.168.1.200:10000 (login with root logins)
Install git (optional)
Using apt-get:
apt-get install git
Install some tools (optional)
Using apt-get:
apt-get install mc p7zip-full
Install MySQL
Using apt-get:
apt-get install mysql-server
REMARK: restart MySQL using systemctl restart
mysql.service
Install Apache
Using apt-get:
apt-get install apache2 apache2-mpm-prefork
REMARK: restart Apache using systemctl restart
apache2.service
Install PHP
Using apt-get:
apt-get install php5
Install MySQL Native Driver (mysqlnd)
apt-get install php5-mysqlnd
REMARK: If, for any reason, you don’t want mysqlnd,
try apt-get install php5-mysql instead.
Install php adodb extension (optional).
apt-get install php5-adodb
Install database manager (optional)
phpMyAdmin and adminer are popular. I prefer adminer:
mkdir /var/www/adminer
wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/adminer/adminer-3.6.3-mysql-en.php
REMARK: you can use apt-get install adminer, but
this will remove php5-mysqlnd and install
php5-mysql. See here.
Entrepreneur | Full-stack developer | Founder of MediSign Ltd. I have over 15 years of professional experience designing and developing web applications. I am also very experienced in managing (web) projects.